Dans le paysage en constante évolution de la santé et du bien-être, la notion de graisse viscérale a suscité un intérêt croissant ces dernières années. Ce type de graisse, insaisissable et souvent méconnu, a fait l'objet de recherches approfondies, car il est lié à une multitude de problèmes de santé graves. À mesure que nous approfondissons les subtilités de la graisse viscérale, il devient de plus en plus évident que comprendre et traiter cette menace cachée pour la santé est crucial pour maintenir un bien-être optimal.
Qu'est-ce que la graisse viscérale ?
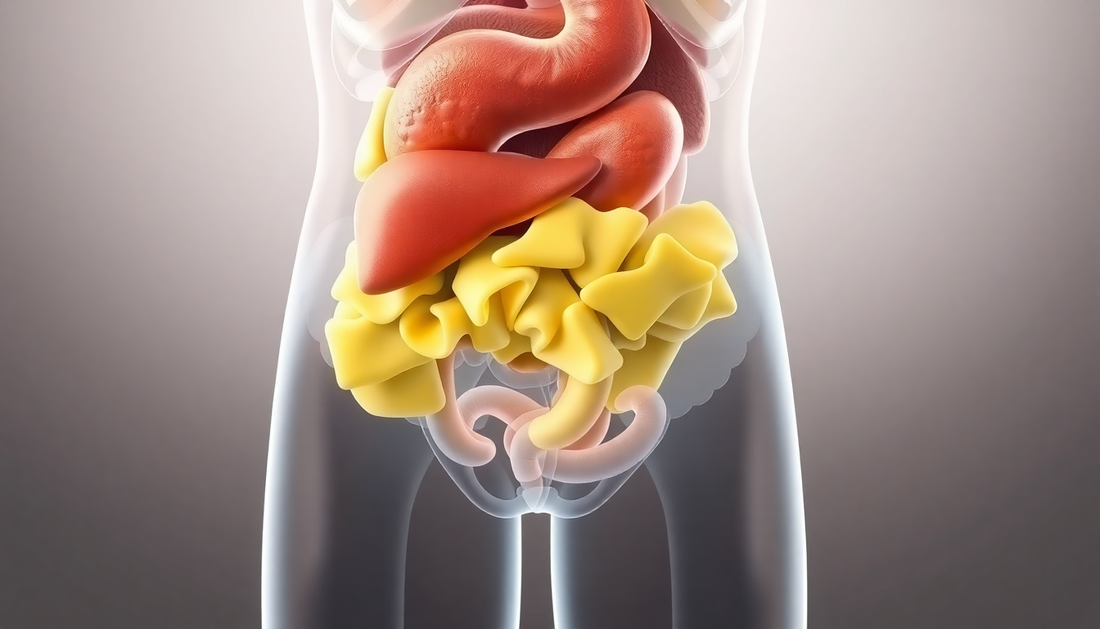
La graisse viscérale, souvent appelée « graisse abdominale », est un type de graisse unique qui s'accumule profondément dans la cavité abdominale, entourant des organes vitaux comme le foie, les reins et les intestins. Contrairement à la graisse sous-cutanée, située juste sous la peau, la graisse viscérale est plus difficile à détecter et peut avoir un impact important sur la santé globale.
La graisse viscérale est composée de tissu adipeux, un type de tissu conjonctif spécialisé qui stocke l'énergie sous forme de lipides. Ce type de graisse est particulièrement actif sur le plan métabolique, ce qui signifie qu'il peut libérer diverses hormones et substances inflammatoires pouvant avoir des conséquences importantes sur l'organisme.
Pourquoi la graisse viscérale est-elle dangereuse ?
La principale raison pour laquelle la graisse viscérale est considérée comme si dangereuse est sa proximité avec les organes vitaux et sa capacité à perturber leur fonctionnement normal. En s'accumulant, la graisse viscérale peut exercer une pression sur les organes environnants, entraînant divers problèmes de santé.
L'un des risques les plus importants associés à la graisse viscérale est son lien avec le développement de la résistance à l'insuline et du diabète de type 2. On pense que la graisse viscérale interfère avec la capacité de l'organisme à utiliser efficacement l'insuline, une hormone responsable de la régulation de la glycémie. Cela peut entraîner l'apparition d'une résistance à l'insuline, précurseur du diabète de type 2.
De plus, il a été démontré que la graisse viscérale contribue au développement des maladies cardiovasculaires. Les substances inflammatoires libérées par la graisse viscérale peuvent endommager la paroi des vaisseaux sanguins, entraînant l'accumulation de plaque et le rétrécissement des artères. Ceci peut, à son tour, augmenter le risque de crise cardiaque, d'accident vasculaire cérébral et d'autres complications cardiovasculaires.
Outre ces problèmes métaboliques et cardiovasculaires, la graisse viscérale a également été associée à un risque accru de certains types de cancer, comme le cancer du côlon et le cancer du sein chez les femmes ménopausées. L'environnement inflammatoire créé par la graisse viscérale jouerait un rôle dans le développement et la progression de ces tumeurs malignes.
Déterminer si vous avez de la graisse viscérale
Identifier la présence de graisse viscérale peut s'avérer complexe, car elle n'est pas toujours visible à l'œil nu. Cependant, plusieurs méthodes permettent d'évaluer la quantité de graisse viscérale présente dans le corps.
L'une des méthodes les plus courantes pour mesurer la graisse viscérale est la mesure du tour de taille. Un tour de taille supérieur à 102 cm (40 pouces) pour les hommes ou 88 cm (35 pouces) pour les femmes est généralement considéré comme un indicateur d'excès de graisse viscérale. Cette mesure peut être utile pour identifier les personnes présentant un risque accru de développer des problèmes de santé liés à la graisse viscérale.
Une autre méthode d'évaluation de la graisse viscérale consiste à recourir à des techniques d'imagerie, telles que la tomodensitométrie (TDM) ou l'imagerie par résonance magnétique (IRM). Ces techniques d'imagerie avancées offrent une vue détaillée des structures internes du corps, permettant aux professionnels de santé de mesurer avec précision la quantité de graisse viscérale présente.
Dans certains cas, les prestataires de soins de santé peuvent également recommander l’utilisation d’une analyse d’impédance bioélectrique (BIA) ou d’une absorptiométrie à rayons X à double énergie (DEXA) pour déterminer la composition de la graisse corporelle, y compris la présence de graisse viscérale.
Stratégies pour réduire la graisse viscérale
Heureusement, il existe plusieurs stratégies efficaces qui peuvent être utilisées pour réduire la graisse viscérale et atténuer les risques pour la santé qui y sont associés.
Modifications alimentaires
L'une des étapes les plus importantes pour lutter contre la graisse viscérale est d'adopter une alimentation saine et équilibrée. Cela comprend :
- Augmenter la consommation d’aliments entiers et riches en nutriments, tels que les fruits, les légumes, les céréales complètes et les protéines maigres.
- Limiter la consommation d’aliments transformés, riches en calories et en sucre, qui peuvent contribuer à l’accumulation de graisse viscérale.
- Incorporer des graisses saines, comme celles présentes dans les avocats, les noix et l’huile d’olive, qui peuvent aider à réduire l’inflammation et à soutenir la santé métabolique globale.
- Restez hydraté en buvant beaucoup d’eau tout au long de la journée.
Stratégies d'exercice
Une activité physique régulière est un autre élément essentiel pour lutter contre la graisse viscérale. Combiner exercices aérobiques et musculation peut être particulièrement efficace pour cibler et réduire la graisse viscérale. Voici quelques exercices recommandés :
- Les activités cardiovasculaires, comme la marche rapide, le jogging, le vélo ou la natation, peuvent aider à brûler des calories et à améliorer la santé cardiovasculaire globale.
- Exercices de musculation, comme l’haltérophilie ou les exercices de poids corporel, qui peuvent aider à développer la masse musculaire et à stimuler le métabolisme.
- L’entraînement par intervalles à haute intensité (HIIT), qui consiste à alterner des périodes d’exercice intense avec des périodes de repos ou d’activité de faible intensité, peut être un moyen efficace de cibler la graisse viscérale.
Modifications du mode de vie
Outre les stratégies diététiques et sportives, certains changements de mode de vie peuvent également contribuer à la réduction de la graisse viscérale. Parmi ceux-ci, on peut citer :
- Privilégiez les techniques de gestion du stress, telles que la méditation, le yoga ou les exercices de respiration profonde, car le stress chronique peut contribuer à l’accumulation de graisse viscérale.
- Assurer un sommeil adéquat, car le manque de sommeil a été associé à une augmentation des niveaux de graisse viscérale.
- Éviter ou limiter la consommation d’alcool, car une consommation excessive d’alcool peut entraîner une accumulation de graisse viscérale.
Conclusion
La graisse viscérale est un problème de santé complexe et souvent mal compris, mais qui mérite toute notre attention. En comprenant les dangers associés à ce type de graisse et en adoptant une approche globale pour la réduire, chacun peut prendre des mesures proactives pour préserver sa santé et son bien-être à long terme.
Grâce à une combinaison d'adaptations alimentaires, de stratégies d'exercice et de changements de mode de vie, il est possible de gérer et de réduire efficacement la graisse viscérale, diminuant ainsi le risque de complications graves. En accordant la priorité à cet aspect de notre santé, nous pouvons vivre une vie plus épanouissante et plus saine, libérés des contraintes de cette menace cachée.